GENETIC CODE
What is DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA, is the most basic organic structure of all living organisms and some viruses in the world. DNA molecules are found in the cell nucleus and contain encoded information during the formation of all proteins in living things.
As in all living things and in humans, our genetic structure is on the basis of growth, development, reproduction and aging where this hereditary structure known as DNA (DeoxyriboNucleic Acid). DNA contains the codes of our lives that make us who we are, make us different from others, or have a primary role in many hereditary diseases that we get.
Structure of DNA
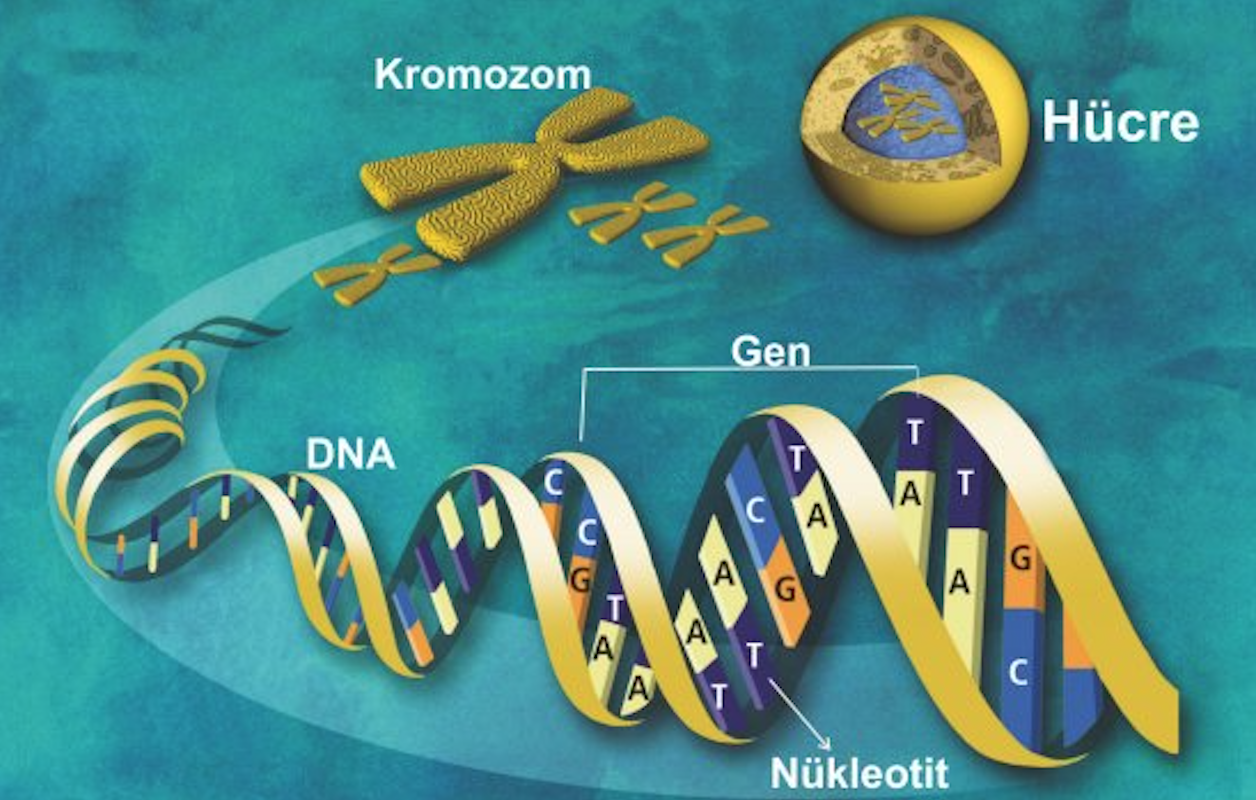
Nucleotides are organic molecules that forms DNA. Each nucleotide composed from a Phosphate group, a Sugar group and a Nitrogenous Base group. These 4 base groups are the basic building blocks of DNA which called Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymine (T) and Cytosin (C). These 4 letters (base group) are connected to each other by hydrogen bonds, the structure of the DNA is similar to the spiral stairs , and the bases arranged on the steps of this ladder are always connected to each other in the form of A-G and T-C. Phosphates and sugar form the arms of the stairs (Double Helix Structure).
The sequence of these 4 base letters form the information in the DNA which is our genetic code. Each person has their own genetic code called GENOME. We can call this GENOME person's own book. This 4 basic letters form groups of 3, namely words (CODONs), which form one of the 20 amino acids found in our bodies. These amino acids, which are the basic building blocks of life, form proteins. Certain amino acid sequences (words) combine to form sentences called GENEs.
The entire human GENOME consists of 3 billion 200 million A, G, T, C letters specific to each person, which make up approximately 30,000 GENEs. When we open the DNA molecule in a cell, it reaches 2 meters in length. DNA molecules that are tightly wrapped together within the cell form CHROMOSOMES (ie parts of the book). There are 46 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus of a human cell where we take half of these couples (23) from our mother and half (23) from our father.
Discovery of DNA
DNA allows us to transfer the characteristics that we have received from predecessors and pass to our next generations. Genetic scientists who were investigating our inherited (hereditary) family traits and diseases, gathered the information obtained until by 1953 and form a model of DNA molecule. James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the double-stranded DNA in 1953 and won the Nobel Prize in Medicine.
The “Human Genome Project’’ which includes the studies of human genetic structure, the genetic code of human DNA sequence (A: Adenine, G: Guanine, T: Thymine, C: Cytosine) was completed and published on April 24, 2003. After 50 years of the discovery of DNA structure April 25th is celebrated as “World DNA Day’’. WORLD DNA DAY has been celebrated in the world since 2003, in our country since 2011 and in our center AGTC in Antalya since 2014.
DNA in the Diagnosis of Diseases
DNA consists of 3 billion 200 million A, G, T, C letters specific to each individual. With the Human Genome Project, developing technology and scientific studies, these specific letters analyzed by decoding Genetic Codes (genes and chromosomes) of individuals and perform different genetic tests like;
- Diagnostic testing is used to precisely identify the disease or the severity of a disease
- Predictive and pre-symptomatic genetic tests are used to find gene changes that increase a person's likelihood of developing diseases.
- Carrier testing is used to find people who "carry" a change in a gene that is linked to disease
- Prenatal testing is offered during pregnancy to help identify fetuses that have certain diseases
- Newborn screening is used to test babies one or two days after birth to find out if they have certain diseases known to cause problems with health and development
- Pharmacogenomic testing gives information about how certain medicines are processed by an individual's body.
- Forensic testing uses DNA sequences to identify biological relationships between people
How DNA Tests are Performed and Evaluated?
Once a person decides to proceed with genetic testing, a medical geneticist, primary care doctor, specialist, or nurse practitioner can order the test. Genetic testing is often done as part of a genetic consultation. Before a person has a genetic test, it is important that he or she understands the testing procedure, the benefits and limitations of the test, and the possible consequences of the test results. The process of educating a person about the test and obtaining permission is called informed consent.
Genetic tests are performed on a sample of blood, saliva, hair, skin, amniotic fluid (the fluid that surrounds a fetus during pregnancy), or other tissue. DNA extraction done from these samples and analysis can be done.
Genetic diagnostic methods are mainly divided into two;
1. Cytogenetic and Molecular Cytogenetic Methods
Numerical or structural defects of chromosomes are determined by these methods using karyotyping and cytogenetic banding techniques. FISH (Fluorescent in situ hybridization) and CGH (Comparative genomic hybridization) methods are used in molecular cytogenetic methods.
2. Molecular Genetic Diagnosis Methods
In molecular genetic diagnostic methods, a single gene and / or short fragments of DNA and / or the entire genome are used to analyze, variations and mutations leading to any genetic disease; These methods include;
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) & Real Time PCR
- Microarray
- DNA Sequencing (Sanger Sequencing, New Generation Sequencing)
A person who applied for a genetic test to our center; firstly registration process of the person is done and interperation of the family and medical history listened detaily to draw the family tree (pedigree). A detailed physical examination is then performed to reveal the person's medical findings. Physical findings are evaluated for an inherited disease in the family. After writing the clinical report and phenotypic characteristics of the person, he/she and families are informed about the Genetic Test method, procedure, the benefits and limitations of the test, the possible results of the test, after the person or parents sign the ‘’genetic test consent form’’ the sample (blood, salive etc..) is taken in appropriate condition. After that, in the laboratory environment , DNA extraction is performed and the genes of the related diseases are examined by using the relevant DNA analysis methods.
After the relevant genetic analysis has been examined, genetic counseling is given by detailed interpretation of the results. In addition, with the physician of the patient clinical and molecular aspects of the patient and the results are discussed mutually and the diagnosis of the patient becomes clear and the treatment method is determined more clearly by the physician.
AGTC Ltd. Şti is established with the influence of the four bases that forms DNA (Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymine (T) and Cytosin (C)) as ‘’Antalya Genetic Diseases Diagnosis Center’’ and serves individuals with the motto of ''Your Genetic Code, Your Life Quality''.
For more information and for your GENETIC CODE you can contact with our center.
